Correct answer: A). The enzyme influences the speed of change from substrate to product The enzymes are the biological catalyst that speed up the rate of chemical reactions by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction pathway. They increase the speed of change of substrate to the product and it remains unchanged in the reaction.
Enzyme Concept Maps | Templates and Examples
8.6: Enzymes. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is called a catalyst, and the molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions are called enzymes. Most enzymes are proteins and perform the critical task of lowering the activation energies of chemical reactions inside the cell.

Source Image: scitechdaily.com
Download Image
Key Terms Enzyme structure and function Enzymes are catalysts. They are usually proteins, though some RNA molecules act as enzymes too. Enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction – that is the required amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur.

Source Image: proprofs.com
Download Image
Explore Enzyme Activity with Toothpicks | STEM Activity Enzymatic action can aid this process. The enzyme–substrate complex can lower the activation energy by contorting substrate molecules in such a way as to facilitate bond-breaking, helping to reach the transition state. Finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Which Statement Describes How Enzymes And Substrates Are Related
Enzymatic action can aid this process. The enzyme–substrate complex can lower the activation energy by contorting substrate molecules in such a way as to facilitate bond-breaking, helping to reach the transition state. Finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. As the enzyme and substrate come together, their interaction causes a mild shift in the enzyme’s structure that confirms an ideal binding arrangement between the enzyme and the substrate. This dynamic binding maximizes the enzyme’s ability to catalyze its reaction. Figure 6.10.1 6.10. 1: Induced Fit: According to the induced fit model, both
Lock and key model is used to describe the mechanism of enzyme action. This model was first proposed by German chemis… | Teaching biology, Lock and key, School work
Biology 1st Edition • ISBN: 9780132013499 Kenneth R. Miller, Levine 2,470 solutions Biology Catalysing chemical reactions with enzymes — Science Learning Hub
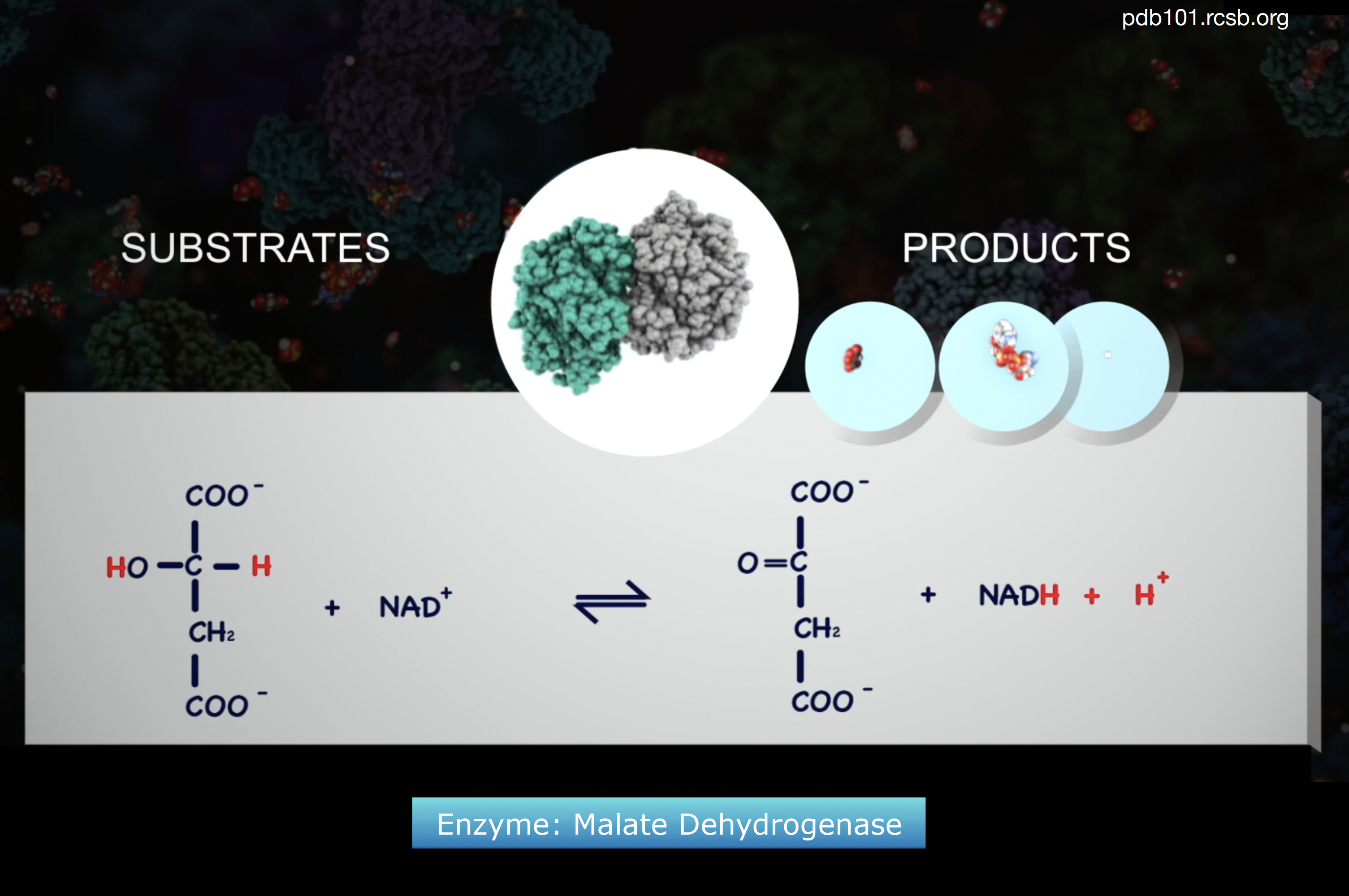
Source Image: sciencelearn.org.nz
Download Image
Enzymes (Updated) – YouTube Biology 1st Edition • ISBN: 9780132013499 Kenneth R. Miller, Levine 2,470 solutions Biology

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
Enzyme Concept Maps | Templates and Examples Correct answer: A). The enzyme influences the speed of change from substrate to product The enzymes are the biological catalyst that speed up the rate of chemical reactions by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction pathway. They increase the speed of change of substrate to the product and it remains unchanged in the reaction.

Source Image: edrawmind.wondershare.com
Download Image
Explore Enzyme Activity with Toothpicks | STEM Activity Key Terms Enzyme structure and function Enzymes are catalysts. They are usually proteins, though some RNA molecules act as enzymes too. Enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction – that is the required amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur.

Source Image: sciencebuddies.org
Download Image
Analyzing Graphics: Enzymes | Biology corner, Cell biology, Biology The particular substrate–enzyme complex (what is formed when a substrate binds to an enzyme’s active site) has a certain function or makes a certain end product. Soooooo, if that particular enzyme did not have its correct molecular architecture (3D shape), the correct substrate could not bind to the correct active site/enzyme and therefore, the

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Biology Quiz: Trivia Questions On Enzymes! – Trivia & Questions Enzymatic action can aid this process. The enzyme–substrate complex can lower the activation energy by contorting substrate molecules in such a way as to facilitate bond-breaking, helping to reach the transition state. Finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself.

Source Image: proprofs.com
Download Image
Enzymes Biochemistry Trivia Quiz! – Trivia & Questions As the enzyme and substrate come together, their interaction causes a mild shift in the enzyme’s structure that confirms an ideal binding arrangement between the enzyme and the substrate. This dynamic binding maximizes the enzyme’s ability to catalyze its reaction. Figure 6.10.1 6.10. 1: Induced Fit: According to the induced fit model, both
(77).jpg)
Source Image: proprofs.com
Download Image
Enzymes (Updated) – YouTube
Enzymes Biochemistry Trivia Quiz! – Trivia & Questions 8.6: Enzymes. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is called a catalyst, and the molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions are called enzymes. Most enzymes are proteins and perform the critical task of lowering the activation energies of chemical reactions inside the cell.
Explore Enzyme Activity with Toothpicks | STEM Activity Biology Quiz: Trivia Questions On Enzymes! – Trivia & Questions The particular substrate–enzyme complex (what is formed when a substrate binds to an enzyme’s active site) has a certain function or makes a certain end product. Soooooo, if that particular enzyme did not have its correct molecular architecture (3D shape), the correct substrate could not bind to the correct active site/enzyme and therefore, the